关于CurieNeurons
CurieNeurons,即Curie神经元,
Neurons能通过示例学习,不用编程,可以通过数据离线学习。
能自主发现新内容或异常。
general-vision提供了两个版本的下载,免费版和专业版,专业版售价19美刀。
免费版下载:
http://pan.baidu.com/s/1jI8kOaa
收费版购买:
http://www.general-vision.com/products/curieneurons/
免费版与收费版区别:
CurieNeurons
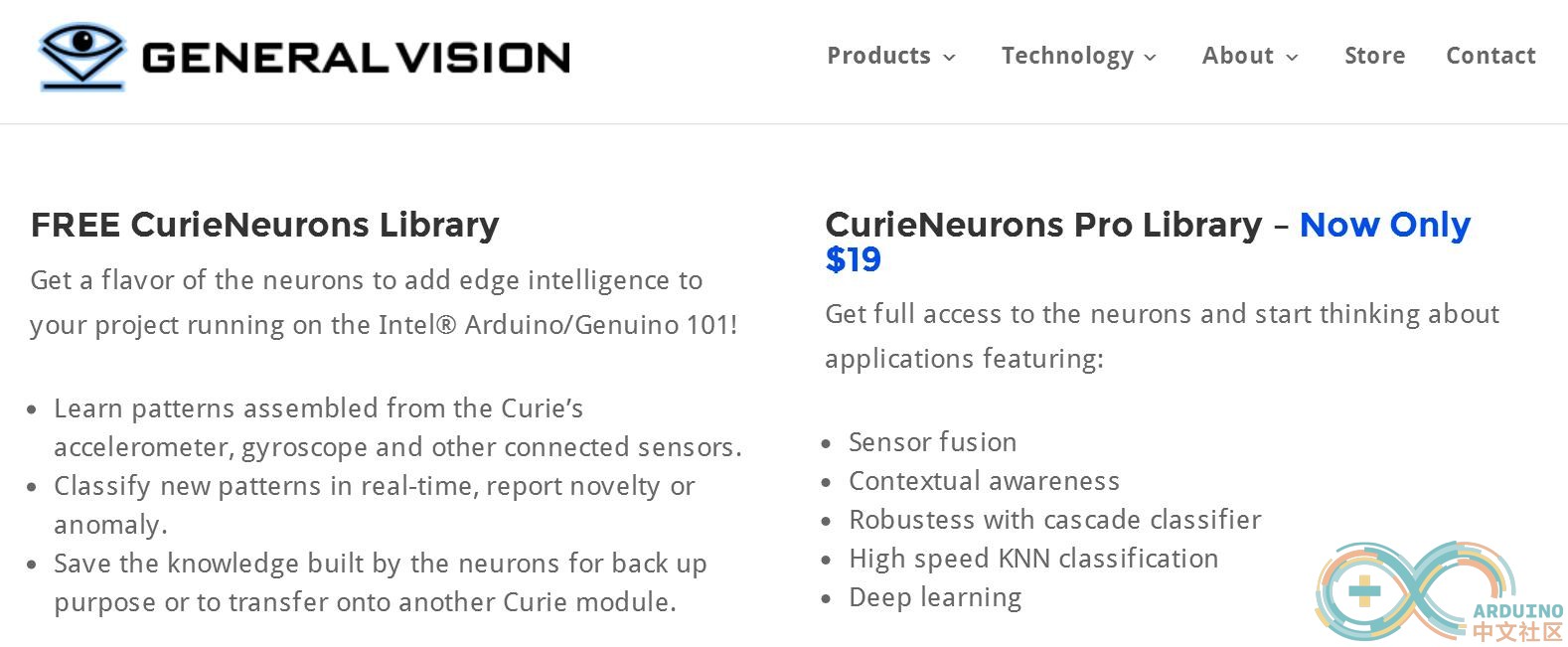
从字面上理解,就是收费版对动作的识别能更准确。我已经买了收费版,粗略的看了下库,两个版本并没有多大区别,猜测收费版只是添加了传感器数据融合,让数据更为准确。所以暂时不建议大家购买。
下载并通过IDE导入库:
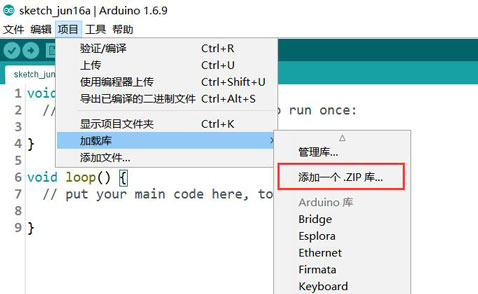
现在我们可以开始我们牛逼哄哄的神经元编程之旅了。
[mw_shl_code=cpp,true]/*
* ===============================================
Example sketch using the Intel CurieIMU library and the General Vision CurieNeurons library
for Intel(R) Curie(TM) devices
Motion is converted into a simple feature vector as follows:
[ax'1, ay'1, az'1, gx'1,gy'1, gz'1, ax'2, ay'2, az'2, gx'2, gy'2, gz'2, ...] over a number of time samples
Note that the values a' and g' are normalized and expand between the running min and max of the a and g signals.
After calibration is made,
Use the serial monitor to edit the category of a motion,
(ex= 1 for vertical, 2 for horizontal, 0 for stillness or anything else),
Start moving the Curie in an expected direction,
and when you press Enter the last feature vector is learned.
Note that this "snapshot" approach is simplistic and you may have to teach several times
a given motion so the neurons store models with different amplitudes, acceleration, etc.
Ideally we want to learn consecutives vectors for a few seconds.
===============================================
*/
#include "CurieIMU.h"
int ax, ay, az; // accelerometer values
int gx, gy, gz; // gyrometer values
int calibrateOffsets = 1; // int to determine whether calibration takes place or not
#include <CurieNeurons.h>
CurieNeurons hNN;
int catL=0; // category to learn
int prevcat=0; // previously recognized category
int dist, cat, nid, nsr, ncount; // response from the neurons
//
// Variables used for the calculation of the feature vector
//
#define sampleNbr 10 // number of samples to assemble a vector
#define signalNbr 6 // ax,ay,az,gx,gy,gz
int raw_vector[sampleNbr*signalNbr]; // vector accumulating the raw sensor data
byte vector[sampleNbr*signalNbr]; // vector holding the pattern to learn or recognize
int mina=0xFFFF, maxa=0, ming=0xFFFF, maxg=0, da, dg;
void setup()
{
Serial.begin(9600); // initialize Serial communication
while (!Serial); // wait for the serial port to open
// initialize device
Serial.println("Initializing IMU device...");
CurieIMU.begin();
// use the code below to calibrate accel/gyro offset values
if (calibrateOffsets == 1)
{
Serial.println("About to calibrate. Make sure your board is stable and upright");
delay(5000);
Serial.print("Starting Gyroscope calibration and enabling offset compensation...");
CurieIMU.autoCalibrateGyroOffset();
Serial.println(" Done");
Serial.print("Starting Acceleration calibration and enabling offset compensation...");
CurieIMU.autoCalibrateAccelerometerOffset(X_AXIS, 0);
CurieIMU.autoCalibrateAccelerometerOffset(Y_AXIS, 0);
CurieIMU.autoCalibrateAccelerometerOffset(Z_AXIS, 1);
Serial.println(" Done");
}
// Initialize the neurons and set a conservative Max Influence Field
hNN.Init();
hNN.Forget(1000); //set a conservative Max Influence Field prior to learning
int value=hNN.MAXIF(); // read the MAXIF back to verify proper SPI communication
Serial.print("\nMaxif register=");Serial.print(value);
Serial.print("\n\nEntering loop...");
Serial.print("\nMove the module vertically or horizontally...");
Serial.print("\ntype 1 + Enter if vertical motion");
Serial.print("\ntype 2 + Enter if horizontal motion");
Serial.print("\ntype 0 + Enter for any other motion");
}
void loop()
{
// Learn if push button depressed and report if a new neuron is committed
if (Serial.available() == 2)
{
catL = Serial.read();
char inChar = (char)Serial.read();
if (inChar == '\n')
{
catL = catL - 48;
Serial.print("\nLearning motion category "); Serial.print(catL);
// learn 5 consecutive sample vectors
for (int i=0; i<5; i++)
{
getVector(); // the vector array is a global
//Serial.print("\nVector = ");
//for (int i=0; i<signalNbr*sampleNbr; i++) {Serial.print(vector);Serial.print("\t");}
ncount=hNN.Learn(vector, sampleNbr*signalNbr, catL);
}
Serial.print("\tNeurons="); Serial.print(ncount);
}
}
else
{
// Recognize
getVector(); // the vector array is a global
hNN.Classify(vector, sampleNbr*signalNbr,&dist, &cat, &nid);
if (cat!=prevcat)
{
if (cat!=0x7FFF)
{
Serial.print("\nMotion category #"); Serial.print(cat);
}
else Serial.print("\nMotion unknown");
prevcat=cat;
}
}
}
void getVector()
{
// the reset of the min and max values is optional depending if you want to
// use a running min and max from the launch of the script or not
mina=0xFFFF, maxa=0, ming=0xFFFF, maxg=0, da, dg;
for (int sampleId=0; sampleId<sampleNbr; sampleId++)
{
//Build the vector over sampleNbr and broadcast to the neurons
CurieIMU.readMotionSensor(ax, ay, az, gx, gy, gz);
// update the running min/max for the a signals
if (ax>maxa) maxa=ax; else if (ax<mina) mina=ax;
if (ay>maxa) maxa=ay; else if (ay<mina) mina=ay;
if (az>maxa) maxa=az; else if (az<mina) mina=az;
da= maxa-mina;
// update the running min/max for the g signals
if (gx>maxg) maxg=gx; else if (gx<ming) ming=gx;
if (gy>maxg) maxg=gy; else if (gy<ming) ming=gy;
if (gz>maxg) maxg=gz; else if (gz<ming) ming=gz;
dg= maxg-ming;
// accumulate the sensor data
raw_vector[sampleId*signalNbr]= ax;
raw_vector[(sampleId*signalNbr)+1]= ay;
raw_vector[(sampleId*signalNbr)+2]= az;
raw_vector[(sampleId*signalNbr)+3]= gx;
raw_vector[(sampleId*signalNbr)+4]= gy;
raw_vector[(sampleId*signalNbr)+5]= gz;
}
// normalize vector
for(int sampleId=0; sampleId < sampleNbr; sampleId++)
{
for(int i=0; i<3; i++)
{
vector[sampleId*signalNbr+i] = (((raw_vector[sampleId*signalNbr+i] - mina) * 255)/da) & 0x00FF;
vector[sampleId*signalNbr+3+i] = (((raw_vector[sampleId*signalNbr+3+i] - ming) * 255)/dg) & 0x00FF;
}
}
}[/mw_shl_code]
待写
以后我也可以装逼说,我在做深度学习了!
|